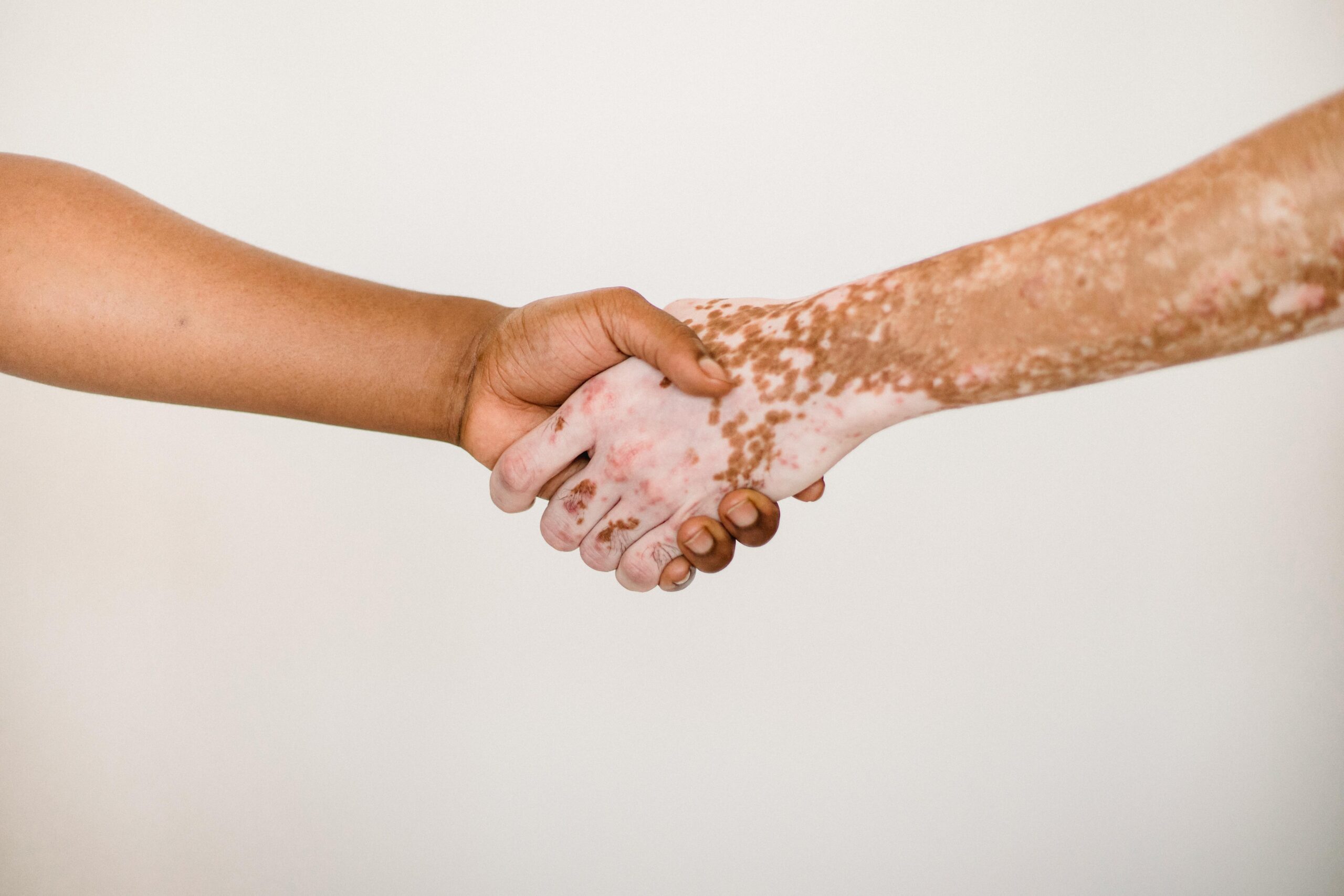
Empower Your Health: Evaluating to Understanding Autoimmune Support, put simple.
By providing clear information about immune disorders, this blog post aims to educate and empower readers to better understand and simply educate about these complex conditions.
In recent years, autoimmune diseases have garnered increasing attention within the world of healthcare and wellness. These complex conditions occur when the immune system, the body’s defense mechanism against harmful invaders, mistakenly attacks its cells, tissues, and organs. From rheumatoid arthritis and lupus to multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes, autoimmune diseases encompass a diverse array of disorders that can impact nearly every system in the body in a very painful way.
Despite their prevalence and significant impact on individuals’ lives, autoimmune diseases remain widely misunderstood. Many people are unaware of the intricacies involved in these conditions, leading to misconceptions and challenges in diagnosis, treatment, and management.
In this land of healthcare, it becomes essential to shed light on the lesser-known aspects of autoimmune issues. Beyond the surface-level understanding commonly presented, exists a wealth of insights, experiences, and advancements that can profoundly impact individuals with autoimmune diseases.
This exploration aims to uncover the truths often overlooked or underrepresented in mainstream discussions about autoimmune conditions. By delving into these topics, we seek to provide valuable knowledge, support, and empowerment to those affected by autoimmune issues.
What Are Immune Disorders? Immune disorders, known as immunological disorders or immune system disorders, occur when the body’s immune system malfunctions. Instead of protecting the body from harmful invaders like bacteria and viruses, the immune system may attack healthy cells and tissues, leading to various health problems. Certain autoimmunities are sadly often painfully chronic and uncurbable.
Types of Immune Disorders:
- Autoimmune diseases are conditions characterized by the immune system’s misidentification of the body’s tissues as foreign invaders, leading to immune attacks against healthy cells and tissues. This immune system dysfunction results in chronic inflammation and tissue damage, contributing to a range of health problems such as flare-ups. There is so much that can be said about the causes and symptoms
- Flare-ups: are a sudden increase in the severity of symptoms of chronic medical conditions. It can involve intensified pain, swelling, inflammation, or other symptoms that were previously under control or less severe. Flare-ups can be triggered by various factors, such as stress, infections, certain foods, physical activity, or changes in medication. Management often involves adjusting treatment plans, rest, and avoiding known triggers to help reduce the frequency and severity of these episodes.
- Immunodeficiency disorders refer to a group of conditions characterized by a weakened or impaired immune system, resulting in a decreased ability to defend against infections and diseases. In individuals with immunodeficiency disorders, the immune system may be compromised due to various factors, such as genetic mutations, underlying medical conditions, or medical treatments. As a result, these individuals are more vulnerable to infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other pathogens. Examples of immunodeficiency disorders include HIV/AIDS, a viral infection that targets the immune system’s CD4 cells, leading to progressive immune system deterioration and increased susceptibility to opportunistic infections and cancers; and primary immunodeficiency disorders, a group of genetic disorders that affect the development or function of immune cells, making individuals more prone to recurrent or severe infections from infancy or childhood onward. Management of immunodeficiency disorders typically involves a combination of supportive care, such as prophylactic antibiotics and immunoglobulin replacement therapy, and targeted interventions to prevent and treat infections and complications. Early diagnosis and appropriate medical management are essential for optimizing outcomes and improving the quality of life in individuals with immunodeficiency disorders.

Symptoms of Immune Disorders: immune disorders can vary widely depending on the specific condition and the organs or systems affected. However, common symptoms may include:
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness or lack of energy that’s not relieved by rest.
- Recurrent Infections: Frequent or severe infections, such as respiratory infections, urinary tract infections, or skin infections, due to a weakened or dysfunctional immune system.
- Inflammation: Swelling, redness, heat, and pain in affected areas of the body, often a result of chronic inflammation associated with autoimmune diseases.
- Joint Pain and Swelling: Pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, may be a symptom of underlying autoimmune conditions.
- Skin Rashes: Rash or skin irritation, characterized by redness, itching, or flaking, which may occur in conditions like eczema or psoriasis.
- Digestive Problems: Symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, or malabsorption of nutrients, which may be present in autoimmune diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
- Neurological Symptoms: such as headaches, dizziness, numbness or tingling sensations, muscle weakness, or cognitive difficulties, which may occur in conditions like multiple sclerosis or Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant and unintentional weight loss, which can occur in autoimmune diseases due to metabolic changes or loss of appetite.
- Other Systemic Symptoms: Additional systemic symptoms such as fever, night sweats, swollen lymph nodes, or general malaise, which may accompany immune disorders affecting multiple organ systems.

Causes of Immune Disorders: The exact causes of immune disorders are often complex and multifactorial. Potential contributing factors may include:
- Genetic Factors: Many immune disorders have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. Certain genetic mutations or variations may predispose individuals to developing immune system dysfunctions or increase their susceptibility to specific autoimmune or immunodeficiency disorders.
- Environmental Triggers: Environmental factors play a significant role in triggering or exacerbating immune disorders. These triggers can include infections (viral, bacterial, fungal, or parasitic), exposure to allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander, etc.), environmental pollutants (air pollution, chemicals, toxins), dietary factors (gluten, dairy, processed foods), and lifestyle factors (smoking, stress, lack of sleep, sedentary lifestyle).
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those occurring during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause, can influence immune system function and contribute to the development or exacerbation of immune disorders. Hormonal imbalances may affect immune cell activity, cytokine production, and inflammation levels.
- Infections: Certain infections, particularly viral infections, can trigger or exacerbate immune disorders by stimulating the immune system or disrupting immune function. For example, infections with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), cytomegalovirus (CMV), or human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) have been implicated in the development of autoimmune diseases like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) or multiple sclerosis (MS).
- Medications and Treatments: Some medications and medical treatments can affect immune system function and increase the risk of immune disorders. Examples include immunosuppressive drugs (used to treat autoimmune diseases or prevent organ rejection after transplantation), chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and certain biological therapies.
- Age and Gender: Immune disorders may occur at any age but often have different patterns of onset and prevalence depending on age and gender. For example, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus are more common in women of childbearing age, while certain immunodeficiency disorders may be more prevalent in children or older adults.
- Psychosocial Factors: Psychological stress, trauma, and other psychosocial factors can influence immune system function and contribute to the development or exacerbation of immune disorders. Chronic stress, in particular, can dysregulate immune responses and increase susceptibility to infections and inflammatory conditions
- Inflammation: Stress triggers the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase inflammation in the body. For individuals with autoimmune diseases, this can lead to flare-ups and worsening of symptoms.
- Impact on Disease Progression: Stress can affect the progression of autoimmune diseases by worsening the symptoms and potentially accelerating the course of the disease. This is particularly true for conditions like multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Behavioral Factors: Stress can lead to behaviors that negatively impact health, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and inadequate sleep. These behaviors can further aggravate autoimmune diseases and hinder recovery.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic stress can contribute to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression, which are common among individuals with autoimmune diseases. This can create a cycle where psychological stress exacerbates physical symptoms, and worsening physical symptoms increase psychological stress.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options: Diagnosing immune disorders typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies which may take months to get results depending on the condition. Treatment options vary depending on the type and severity of the condition but may include:
- Immunosuppressants: Drugs that suppress the activity of the immune system, such as corticosteroids, methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclosporine.
- Biologic Therapies: Targeted therapies that block specific molecules involved in the immune response, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, interleukin inhibitors, or B-cell depleting agents.
- Immunomodulators: Medications that modify the immune system’s response, such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), interferons, or monoclonal antibodies.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed to treat bacterial infections associated with immunodeficiency disorders.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes such as following a healthy diet, regular exercise, practicing stress management techniques, quitting smoking, and avoiding environmental triggers can help support overall immune system health and reduce the risk of exacerbating symptoms.
- Supportive Care: Supportive care measures may include managing symptoms with over-the-counter medications, using supportive devices or equipment, and seeking supportive services such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, or counseling.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Regular monitoring and follow-up with healthcare providers are essential for assessing treatment effectiveness, monitoring disease progression, managing the side effects of medications, and adjusting treatment plans as needed.
You are not crazy; an unknown autoimmune issue is a very real thing. There are cases where young people don’t experience symptoms until their early 20s-30s, despite having no known history of such an illness with perfectly healthy childhoods. While there are many unanswered questions, there is hope for healing and overcoming this condition.
In conclusion, understanding immune disorders is crucial for maintaining optimal health and well-being. Whether you’re living with an autoimmune disease, an immunodeficiency disorder, or an allergic condition, knowing the signs, symptoms, and treatment options can make a significant difference in your quality of life. By recognizing the importance of a balanced immune system and staying informed about the various types of immune disorders, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their health effectively. Remember early detection, proper diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans are key to successfully navigating immune disorders and minimizing their impact on daily life.
While immune disorders can present unique challenges, they do not define who you are. With the right support, resources, and self-care practices, it’s possible to live a fulfilling and meaningful life despite these conditions.
If you suspect you may have an immune disorder or are experiencing concerning symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare professional for evaluation and guidance. Together, we can continue to raise awareness, promote understanding, and support those affected by immune disorders in their journey toward health and wellness.
Call to Action: If you found this blog post helpful, consider sharing it with others who may benefit from learning more about immune disorders. Stay informed, stay empowered, and prioritize your immune health today.
To help encourage a balanced life while in control of an autoimmune disease, check out some of the other articles that delve into general tips here




